What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to all the strategies and techniques that you apply directly within your website’s pages to help search engines like Google understand and rank your content higher in search results. The idea behind on-page SEO is to optimize your web page’s structure, content, and HTML source code to make it more accessible and relevant to search engine algorithms, while also improving user experience (UX). By enhancing these aspects, you increase the chances of your page being discovered by users searching for related content, products, or services.
On-page SEO is crucial because it helps search engines understand what your page is about and how relevant it is to specific search queries. While off-page SEO (like backlinks) and technical SEO (like site speed) are important, on-page SEO ensures that your individual pages are properly optimized to meet the needs of both search engines and users.
Why is On-Page SEO Important?
- Helps Search Engines Understand Content: The more clearly you communicate your page’s content and purpose to search engines, the more likely they are to rank it higher.
- Improves User Experience: Good on-page SEO practices make your website easy to navigate, fast to load, and relevant to the user’s search intent, which reduces bounce rates and increases user engagement.
- Maximizes Visibility: Properly optimized pages are more likely to appear in search engine result pages (SERPs), leading to increased organic traffic.
- Increases Conversion Rates: An optimized page with great user experience and relevant content helps convert visitors into customers or leads.
On-Page SEO Checklist with Examples
1. Title Tag Optimization

The title tag is one of the most basic components of on-page SEO. It tells both look motors and clients what your page is around. It shows up as the clickable feature in look comes about, making it the to begin with thing potential guests see.
Best Practices:
- Include target keywords at the beginning of the title tag.
- Keep the title under 60 characters to avoid truncation in search results.
- Make it descriptive and engaging to encourage clicks.
Example:
Let’s say you’re writing a blog post about the benefits of yoga. Instead of a generic title like “Yoga Benefits,” you can make it more engaging and SEO-friendly by including the keyword and making it more specific:
- Poor Title: “Yoga Benefits”
- Optimized Title: “10 Amazing Benefits of Yoga for Mental and Physical Health”
In this example, we have included the main keyword (“Benefits of Yoga”) and added a compelling, specific angle (“Mental and Physical Health”) to grab attention.
2. Meta Description
The meta description is a short summary that appears below the title tag in search results. While it doesn’t directly affect rankings, it does play a role in increasing your click-through rate (CTR), which can indirectly impact SEO.
Best Practices:
- Write a compelling description of your page’s content.
- Include relevant keywords.
- Keep it under 160 characters so it’s not cut off in search results.
- Use action-oriented language to encourage clicks.
Example:
For the same yoga blog post, an optimized meta description could be:
- Poor Meta Description: “Learn the benefits of yoga.”
- Optimized Meta Description: “Discover 10 science-backed benefits of yoga for mental clarity, flexibility, and overall well-being.”
Notice how the optimized meta description is more specific, engaging, and informative, providing users with more reason to click.
3. Header Tags (H1, H2, H3)
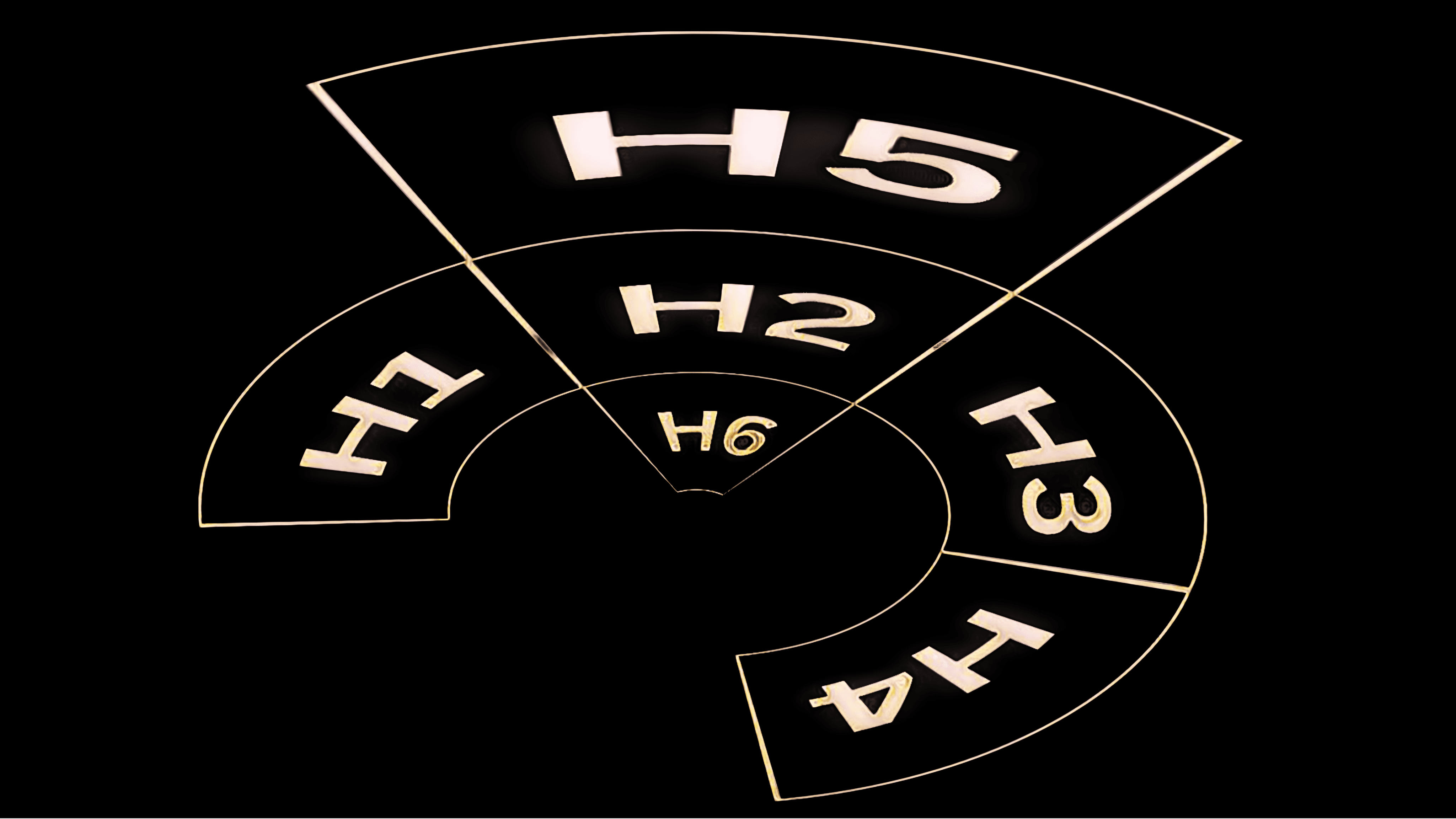
Header tags are used to break up your content and structure it in a way that’s easy to read for both users and search engines. They also help Google understand the hierarchy of information on the page. The H1 tag is the main heading, while H2 and H3 tags are used for subheadings.
Best Practices:
- Use one H1 tag for the main title of the page.
- H2 tags should be used for main subheadings.
- H3 tags can be used for subsections under the H2 headings.
- Include relevant keywords in headers.
Example:
For the yoga blog post, here’s how you could structure your headers:
- H1: “10 Amazing Benefits of Yoga for Mental and Physical Health”
- H2: “What is Yoga?”
- H2: “How Yoga Improves Mental Health”
- H2: “How Yoga Boosts Physical Health”
- H3: “Yoga for Flexibility”
- H3: “Yoga for Stress Relief”
Using these header tags helps both users and search engines understand the structure of your content, improving readability and SEO.
4. URL Structure
URLs should be descriptive, easy to read, and include relevant keywords. A clean URL not only improves SEO but also makes it easier for users to understand what the page is about.
Best Practices:
- Keep URLs short and descriptive.
- Include keywords in the URL.
- Use hyphens to separate words (not underscores).
- Avoid using unnecessary characters (e.g., question marks, numbers).
Example:
- Poor URL:
www.yogablog.com/page1?=123 - Optimized URL:
www.yogablog.com/benefits-of-yoga-for-health
The optimized URL is clear, concise, and includes relevant keywords.
5. Keyword Optimization
Keywords are words or phrases that users enter into search engines to find content. Optimizing your content for relevant keywords helps search engines understand what your page is about and improves its chances of ranking for those keywords.
Best Practices:
- Include your target keyword in key locations like the title, header tags, and body content.
- Avoid keyword stuffing (overusing keywords unnaturally).
- Use semantic variations (synonyms or related terms) to make the content more natural and improve relevancy.
- Use long-tail keywords, which are longer, more specific search queries that typically have lower competition.
Example:
For the yoga post, if your target keyword is “benefits of yoga,” you might include it like this:
- In the title: “10 Amazing Benefits of Yoga for Mental and Physical Health”
- In headers: “How Yoga Improves Mental Health”
- In content: “Yoga is widely recognized for its mental benefits, such as improved focus and reduced anxiety.”
6. Internal Linking
Internal linking refers to linking to other pages within your own website. This helps search engines crawl your site more effectively and boosts the SEO of your linked pages.
Best Practices:
- Link to relevant pages within your site.
- Use descriptive anchor text (the clickable text of the link).
- Avoid excessive internal linking—only link to relevant content.
- Create an internal linking hierarchy (link from high-authority pages to newer or lower-authority pages).
Example:
If you have another post about “Best Yoga Poses for Beginners,” you can link to it from your yoga benefits post like this:
- “If you’re new to yoga, check out our post on best yoga poses for beginners to get started.”
7. Image Optimization
Images make your content more engaging, but large, unoptimized images can slow down page loading times, which hurts both SEO and user experience.
Best Practices:
- Compress images to reduce file size without compromising quality.
- Use descriptive file names (e.g., “yoga-mat-poses.jpg”).
- Include alt text for images, which helps search engines understand the content of the image and makes it accessible for users with visual impairments.
Example:
- Poor Image Filename:
IMG_1234.jpg - Optimized Image Filename:
yoga-poses-for-flexibility.jpg - Alt Text: “A woman practicing yoga poses for flexibility on a yoga mat.”
8. Mobile-Friendliness
With mobile traffic surpassing desktop traffic, it’s essential that your website is optimized for mobile users. Google also uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it will rank the mobile version of your site higher.
Best Practices:
- Use responsive design, so your page automatically adjusts to fit any screen size.
- Test mobile performance regularly using tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Ensure that buttons, text, and forms are easily clickable and readable on small screens.
Example:
Ensure that all text on your page is large enough to read without zooming and that buttons are spaced well for tapping on a mobile screen.
9. Page Load Speed
Page speed is a ranking factor for Google, and faster-loading pages provide a better user experience, leading to higher engagement and lower bounce rates.
Best Practices:
- Compress images and use proper file formats.
- Minimize JavaScript and CSS files.
- Use browser caching to speed up repeated visits.
- Test page speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and implement suggested improvements.
Example:
If your page takes more than 3 seconds to load, users may leave before it even finishes loading, which can harm your SEO. Tools like PageSpeed Insights will give you actionable steps to fix this.
10. User Experience (UX)
Good UX plays a critical role in on-page SEO. If users can easily navigate your site, find what they need, and enjoy their experience, it will lead to better engagement and higher rankings.
Best Practices:
- Ensure **clear
navigation** with easy-to-find menus.
- Make the design visually appealing with readable fonts, balanced colors, and plenty of white space.
- Ensure that the content is easy to scan, with bullet points, subheadings, and short paragraphs.
Example:
A user visiting your yoga page should be able to easily find information about yoga poses, read the content, and explore related topics without feeling overwhelmed.
Conclusion
On-page SEO is a vital aspect of improving your website’s search engine rankings and providing a positive user experience. By following this checklist, you can ensure that your content is optimized for both search engines and users. From optimizing title tags and meta descriptions to improving page speed and mobile-friendliness, each element contributes to the overall SEO success of your site. Consistent and thoughtful optimization can lead to higher search rankings, more traffic, and better conversions over time.
Remember, on-page SEO is not a one-time task. It requires ongoing analysis, testing, and updates to keep your pages aligned with current best practices and search engine algorithms. By continually refining your on-page SEO efforts, you’ll improve both your search engine visibility and the experience you offer to your audience.
